算法基础模板题
在将近期学的模板放到到这里,日后整理出文章
基础模板
给出基础算法的模板题,以及算法的模板。
快速排序
图示:
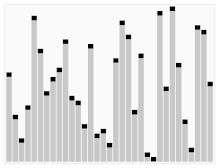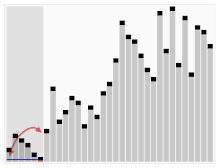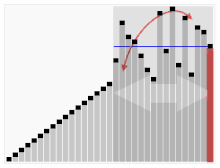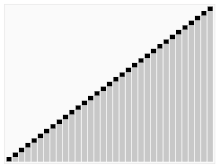
思路
- 快速排序中首先找到 分界点
- 通过分界点 x 实现划分区间 排序 让 x左边的值 小于x 游标的值大于x
- 递归此过程实现排序
注意:
- 选择的分节点是任意的。注意边界的问题如果是 使用的是 quick_sort(a, l, i - 1), quick_sort(a, i , r); 这个边界,那么使用的 temp 的位置就是( l + r + 1) / 2 注意上取整
- 如果使用的是quick_sort(a, l, j), quick_sort(a, j + 1 , r); 这个边界 确定使用的 边界指的位置就是(l + r ) / 2
- 当给定的序列有序时,如果每次选择区间左端点进行划分,每次会将区间[L, R]划分成[L, L]和[L + 1, R],那么相当于每次递归右半部分的区间长度只会减少1,所以就需要递归 n−1次了,时间复杂度会达到 n^2。但每次选择区间中点或者随机值时,划分的两个子区间长度会比较均匀,那么期望只会递归 logn层。
代码:
1 | void quicksort(int q[], int l, int r){ |
1 | void quick_sort(int l, int r){ |
归并排序
图示:
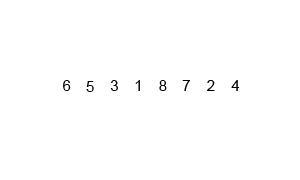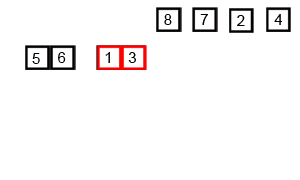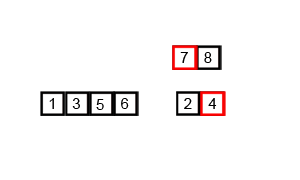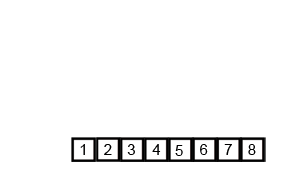
代码:
1 | void merge_sort(int q[], int l, int r){ |
简化版本
1 |
|
代码模板
1 | void merge_sort(int l, int r){ |
时间复杂度分析
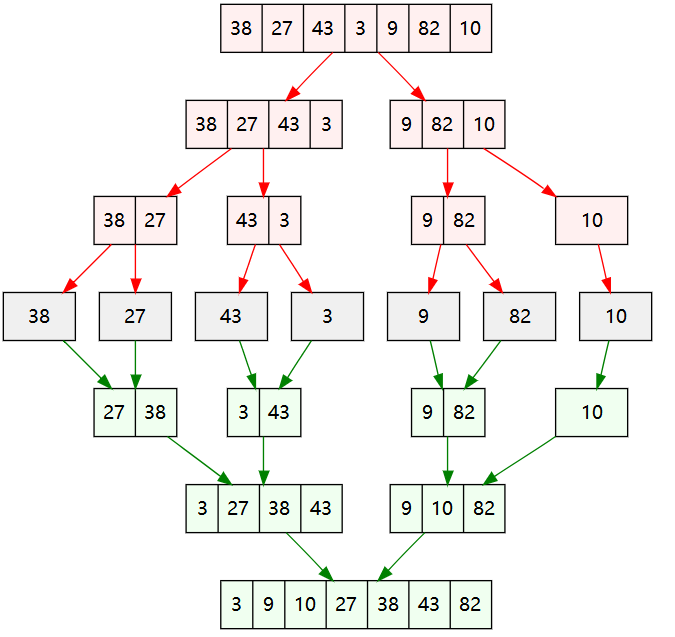
例题逆序对的数量
1 |
|
二分
二分的模板
1 | bool check(int x) {/* ... */} // 检查x是否满足某种性质 |
例题
给定一个按照升序排列的长度为n的整数数组,以及 q 个查询。
对于每个查询,返回一个元素k的起始位置和终止位置(位置从0开始计数)。
如果数组中不存在该元素,则返回“-1 -1”。
输入格式
第一行包含整数n和q,表示数组长度和询问个数。
第二行包含n个整数(均在1~10000范围内),表示完整数组。
接下来q行,每行包含一个整数k,表示一个询问元素。
输出格式
共q行,每行包含两个整数,表示所求元素的起始位置和终止位置。
如果数组中不存在该元素,则返回“-1 -1”。
数据范围
1≤n≤1000001≤n≤100000
1≤q≤100001≤q≤10000
1≤k≤100001≤k≤10000
输入样例:
1 | 6 3 |
输出样例:
1 | 3 4 |
解题代码
1 |
|
例题2 数开三次方计算值(浮点数二分)
1 |
|
高精度计算
之前写过,这里在列举出来
-
大整数的加法计算
方案一:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
using namespace std;
//模拟大数相加的过程
vector<int> add(vector<int> &a, vector<int> &b){
vector<int> ans;
int t = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.size() || i < b.size(); i++){
if (i < a.size()) t += a[i];
if (i < b.size()) t += b[i];
ans.push_back(t % 10);
t /= 10;
}
if (t) ans.push_back(1);
return ans;
}
int main(){
string s1, s2;
cin >> s1 >> s2;
vector<int> a, b;
for (int i = s1.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) a.push_back(s1[i] - '0');
for (int i = s2.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) b.push_back(s2[i] - '0');
auto c = add(a ,b);
for (int i = c.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) cout << c[i];
return 0;
}方案二:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
using namespace std;
string s1, s2, sum;
int main(){
cin >> s1 >> s2;
reverse(s1.begin(), s1.end());
reverse(s2.begin(), s2.end());
int t = 0;
for (int i = 0 ; i < s1.size() || i < s2.size(); i++){
if (i < s1.size()) t += s1[i] - '0';
if (i < s2.size()) t += s2[i] - '0';
sum += t % 10 + '0';
t /= 10;
}
if (t) sum += 1 + '0';
reverse(sum.begin(), sum.end());
cout << sum << end;
return 0;
} -
大整数减法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
using namespace std;
bool cmp(vector<int> &a, vector<int> b){
if (a.size() != b.size()) return a.size() > b.size();
for (int i = a.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--){
if (a[i] != b[i]) return a[i] > b[i];
}
return true;
}
vector<int> sub(vector<int> &a, vector<int> &b){
vector<int> ans;
for (int i = 0, t = 0; i < a.size(); i++){
t = a[i] - t;
if (i < b.size()) t -= b[i];
ans.push_back((t + 10) % 10);
if (t < 0) t = 1;
else t = 0;
}
while(ans.size() > 1 && ans.back() == 0) ans.pop_back();
return ans;
}
int main(){
string s1, s2;
cin >> s1 >> s2;
vector<int> a, b, c;
for (int i = s1.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) a.push_back(s1[i] - '0');
for (int i = s2.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) b.push_back(s2[i] - '0');
if (cmp(a, b))
c = sub(a ,b);
else
c = sub(b, a), cout << "-";
for (int i = c.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) cout << c[i];
return 0;
} -
大整数的乘法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
using namespace std;
vector<int> mul(vector<int> &a, int b){
vector<int> ans;
int t = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.size() || t; i++){
if (i < a.size()) t += a[i] * b;
ans.push_back(t % 10);
t /= 10;
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
string s1;
int b;
vector<int> a;
cin >> s1 >> b;
for (int i = s1.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) a.push_back(s1[i] - '0');
auto c = mul(a, b);
for (int i = c.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) cout << c[i];
return 0;
} -
大整数除法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
using namespace std;
// r代表余数
vector<int> div(vector<int> &a, int b, int &r){
vector<int> ans;
for (int i = a.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--){
r = r * 10 + a[i];
ans.push_back(r / b);
r %= b;
}
reverse(ans.begin(), ans.end());
while (ans.size() > 1 && ans.back() == 0) ans.pop_back();
return ans;
}
int main(){
string s1;
int b, r = 0;
vector<int> a;
cin >> s1 >> b;
for (int i = s1.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) a.push_back(s1[i] - '0');
auto c = div(a, b, r);
for (int i = c.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) cout << c[i];
cout << endl << r << endl;
return 0;
}
前缀和差分
双指针
题目:
给定一个长度为n的整数序列,请找出最长的不包含重复数字的连续区间,输出它的长度。
输入格式
第一行包含整数n。
第二行包含n个整数(均在0~100000范围内),表示整数序列。
输出格式
共一行,包含一个整数,表示最长的不包含重复数字的连续子序列的长度。
数据范围
1≤n≤1000001≤n≤100000
输入样例:
1 | 5 |
输出样例:
1 | 3 |
思路:i指针假设是在左边的的不断枚举的,此时j指针检查不断从右向左枚举检查是否满足性质 j向后移动时删除掉对应不在区间内的数,其中通过s[i] 表示每个数出现的次数 时间复杂度0(n)
1 |
|
位运算
位运算的操作
-
n的二进制整数中第K位是多少?
- 第k位 移动到最后一位 (个位)n >> k
-
查看个位是多少 与 1
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
using namespace std;
int main(){
const int n = 32;
for (int k = 5; k >= 0; k --) printf("%d", n >> k & 1);
return 0;
}
-
lowbit运算(树状数组中基本操作)
返回x的最后一位1所代表的的值是多少?
例如 x 为 101000 则返回 1000
方式: x & -x , -x 表示 补码 就是~x + 1 则 x & (~x + 1 )
x = 1010 … 10…0
~x = 0101… 01…1
~x + 1 = 0101… 10…0
与运算 最后就是 代表最后一位1所代表的的值
补码的原理 x + ( -x) == 0;
-x == 0 - x
0(int类型) 32个0 -x 需要接为1 后32个0 含义就是 ~x + 1
应用 求x(binary)中1的个数
代码实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
using namespace std;
int lowbit(int x){
return x & -x;
}
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n --){
int x, ans = 0;
cin >> x;
while (x) x -= lowbit(x), ans++;
printf("%d ", ans);
}
return 0;
}
离散化
基础 1 课程中:1.07
区间合并
数据结构部分
模拟单链表(数组)
1 |
|
模拟双链表
1 |
|
模拟栈
1 |
|
模拟队列
1 |
|
单调栈的使用
删除逆序的情况, 存放在队列中,存在给定的数列 输出左边的第一个比本身小的数,如果不存在的话 那么就返回 -1
使用暴力的做法:通过使用两重for,对每个数进行枚举,向左边查找如果找到的话就输出 并break, 如果没有的话那么就返回 -1;时间 复杂度为
思路:对于以上的那种方法暴力的做法改进, 如果存在,并且i > j那么 说明在向左边查找的时候一定是不会 使用到的那么此时的 ai就需要删除,如果我们将这些元素存放在,stack中那去不符合以上的条件的数据,那么久删除的话,每一次查找的数字就是栈顶的元素,并且此时的时间 复杂度为
1 |
|
单调队列
思想类似于滑动窗口,给定一定长度的数字序列,窗口的长度为一确定的值,通过让窗口的每次向前移动一个位置找到当前的窗口中最大, 小的值。
数组的保存: 通过是a[i]保存数组序列 ,q[i]为队列的下标
滑动窗口的实现:
1 |
|
KMP的实现
主要思想:找到最长的匹配前缀 后缀 的最大值
1 |
|
trie树
1 |
|
并查集
并查集(Union—Find Set)是一种维护集合的一种数据结构,
支持的操作
- 集合的 合并
- 查找两个数,是否在同一个集合中
核心代码:find的理解, find[3] = 1 表示 3的父节点为 1
通过递归的方式实现路径压缩 核心代码:
1 | int find(int x){ |
例题如下:
-
并查集的基本操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28/*
1.并查集 通过树的形式 将数组结合起来实现 合并 与查询
*/
using namespace std;
int const N = 1e5 + 10;
int p[N];
int main(){
int n, m;
scanf("%d%d",&n, &m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) p[i] = i;
while (m --){
char op[2];
int a, b;
scanf("%s%d%d", op, &a, &b);
//此时区间合并
if (*op == 'M') p[find(a)] = find(b);
else{
if (find(a) == find(b)) puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
}
}
return 0;
} -
连通块的个数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n, m;
int p[N], size[N];
int find(int x){
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int main(){
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
p[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
while (m -- ){
string op;
int a, b;
cin >> op;
if (op == "C"){
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
a = find(a), b = find(b);
if (a != b){
p[a] = b;
size[b] += size[a];
}
}
else if (op == "Q1"){
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
if (find(a) == find(b)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
else{
scanf("%d",&a);
cout << size[find(a)] << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
堆和堆排序
1 |
|
模拟堆(构建最小堆)
堆的两个基本操作 down 操作 将数值较小的点向下移动, up操作将数值较大的带你向上移动。
那么手写堆实现的基本操作为:
- 插入一个数 heap[++size] = k, up(size)
- 输出集合中 当前最小的值 输出h[1]
- 删除集合中最小的数 heap[1] = heap[size–], down(1);
- 删除第k个插入的数 删除 K heap[k] = heap[size], up(k), down(k)
- 修改第k个插入的数,更改为x heap[k] = x, up(k)
维护一个集合,初始时集合为空,支持如下几种操作:
- “I x”,插入一个数x;
- “PM”,输出当前集合中的最小值;
- “DM”,删除当前集合中的最小值(数据保证此时的最小值唯一);
- “D k”,删除第k个插入的数;
- “C k x”,修改第k个插入的数,将其变为x;
现在要进行N次操作,对于所有第2个操作,输出当前集合的最小值。
输入格式
第一行包含整数N。
接下来N行,每行包含一个操作指令,操作指令为”I x”,”PM”,”DM”,”D k”或”C k x”中的一种。
输出格式
对于每个输出指令“PM”,输出一个结果,表示当前集合中的最小值。
每个结果占一行。
输入样例:
1 | 8 |
输出样例:
1 | -10 |
解题代码
1 |
|
哈希表
维护一个集合,支持如下几种操作:
- “I x”,插入一个数x;
- “Q x”,询问数x是否在集合中出现过;
现在要进行N次操作,对于每个询问操作输出对应的结果。
输入格式
第一行包含整数N,表示操作数量。
接下来N行,每行包含一个操作指令,操作指令为”I x”,”Q x”中的一种。
输出格式
对于每个询问指令“Q x”,输出一个询问结果,如果x在集合中出现过,则输出“Yes”,否则输出“No”。
每个结果占一行。
数据范围
1≤N≤1051≤N≤105
−109≤x≤109−109≤x≤109
输入样例:
1 | 5 |
输出样例:
1 | Yes |
解题:
-
拉链法的使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
using namespace std;
const int N = 100003;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
void insert(int x){
//hash
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
e[idx] = x, ne[idx] = h[k], h[k] = idx ++;
}
bool find(int x){
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
for(int i = h[k]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
if (e[i] == x) return true;
return false;
}
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
while(n --){
char op[2];
int x;
scanf("%s %d", op, &x);
if (*op =='I') insert(x);
else{
if(find(x)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
}
return 0;
} -
开放寻址法( )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
using namespace std;
const int N = 200003, null = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int h[N];
int find(int x){
int t = (x % N + N) % N;
while (h[t] != null && h[t] != x){
t ++ ;
if (t == N) t = 0;
}
return t;
}
int main(){
memset(h, 0x3f, sizeof h);
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
while (n -- ){
char op[2];
int x;
scanf("%s%d", op, &x);
if (*op == 'I') h[find(x)] = x;
else{
if (h[find(x)] == null) puts("No");
else puts("Yes");
}
}
return 0;
}
STL的使用
-
vector 变长数组,倍增的思想
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17vector,
size() 返回元素个数
empty() 返回是否为空
clear() 清空
front()/back()
push_back()/pop_back()
begin()/end()
[]
支持比较运算,按字典序
//二维的初始化
vector<vector<int>> dp(n + 1, vector<int>(m + 1));
//结合string
vector<string> t(n, string(n, '.'));
// 使用字典序的方式
vector<int> a(4, 3), b(3, 4);
if (a < b) puts("yes"); -
pair
1
2
3
4pair<int, int>
first, 第一个元素
second, 第二个元素
支持比较运算,以first为第一关键字,以second为第二关键字(字典序) -
string
1
2
3
4
5
6string,字符串
size()/length() 返回字符串长度
empty()
clear()
substr(起始下标,(子串长度)) 返回子串
c_str() 返回字符串所在字符数组的起始地址 -
queue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7queue, 队列
size()
empty()
push() 向队尾插入一个元素
front() 返回队头元素
back() 返回队尾元素
pop() 弹出队头元素 -
priority_queue
1
2
3
4
5priority_queue, 优先队列,默认是大根堆
push() 插入一个元素
top() 返回堆顶元素
pop() 弹出堆顶元素
定义成小根堆的方式:priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> q; -
stack, 栈
1
2
3
4
5size()
empty()
push() 向栈顶插入一个元素
top() 返回栈顶元素
pop() 弹出栈顶元素 -
deque
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9deque, 双端队列
size()
empty()
clear()
front()/back()
push_back()/pop_back()
push_front()/pop_front()
begin()/end()
[] -
set, map, multiset, multimap
基于平衡二叉树(红黑树),动态维护有序序列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15size()
empty()
clear()
begin()/end()
++, -- 返回前驱和后继,时间复杂度 O(logn)
set/multiset
insert() 插入一个数
find() 查找一个数
count() 返回某一个数的个数
erase()
(1) 输入是一个数x,删除所有x O(k + logn)
(2) 输入一个迭代器,删除这个迭代器
lower_bound()/upper_bound()
lower_bound(x) 返回大于等于x的最小的数的迭代器
upper_bound(x) 返回大于x的最小的数的迭代器 -
map
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10map/multimap
insert() 插入的数是一个pair
erase() 输入的参数是pair或者迭代器
find()
[] 注意multimap不支持此操作。 时间复杂度是 O(logn)
lower_bound()/upper_bound()
unordered_set, unordered_map, unordered_multiset, unordered_multimap, 哈希表
和上面类似,增删改查的时间复杂度是 O(1)
不支持 lower_bound()/upper_bound(), 迭代器的++,-- -
bitset
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14bitset, 圧位
bitset<10000> s;
~, &, |, ^
>>, <<
==, !=
[]
count() 返回有多少个1
any() 判断是否至少有一个1
none() 判断是否全为0
set() 把所有位置成1
set(k, v) 将第k位变成v
reset() 把所有位变成0
flip() 等价于~
flip(k) 把第k位取反
图论和搜索
dfs
-
全排列问题:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
using namespace std;
const int N = 10;
int a[N], n;
bool visit[N];
void dfs(int cur){
if (cur == n){
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) printf("%d ", a[i]);
cout << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if (!visit[i]){
a[cur] = i;
visit[i] = true;
dfs(cur + 1);
visit[i] = false;
}
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d", &n);
dfs(0);
return 0;
} -
N—Queens问题
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
using namespace std;
const int N = 20;
bool col[N], dg[N], udg[N];
char q[N][N];
int n;
void dfs(int u){
if (u == n){
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) puts(q[i]);
puts("");
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
if (!col[i] && !dg[u + i] && !udg[n - u + i]){
q[u][i] = 'Q';
col[i] = dg[u + i] = udg[n - u + i] = true;
dfs(u + 1);
col[i] = dg[u + i] = udg[n - u + i] = false;
q[u][i] = '.';
}
}
int main(){
cin >> n;
for (int i= 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
q[i][j] = '.';
dfs(0);
return 0;
}
bfs
迷宫问题:
-
模拟queue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int g[N][N], d[N][N];
int m, n;
pair<int, int> q[N * N], pre[N][N];
// 不使用STL队列方式 同数组的方式模拟 队列
int bfs(){
int hh = 0, tt = 0;
//当前的对头保存的是起始的位置
q[0] = {0, 0};
/**默认设置 -1,表示第一次修改设置为 -1, 而一般是从0的位置添加过去的,其他的位置存在且不为-1的话
* 那么认为不是第一次添过去的,此时就不是最短的路径
**/
memset(d, -1, sizeof d);
// 起始的位置设置为 0
d[0][0] = 0;
// 四个方向向量的 移动位置 上 下 左 右
int dx[4] = {-1, 1, 0, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
// 如果队列中的元素不为空的话
while (hh <= tt){
//取出的对头的 元素 先后移动一位++ 即将对头元素出队列
auto t = q[hh++];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int x = t.first + dx[i], y = t.second + dy[i];
// 如果没有超出边界的话, 并且不是障碍位置 并且是第一次访问的话
if (x < n && x >= 0 && y < m && y >= 0 && g[x][y] == 0 && d[x][y] == -1){
//那么我们就将刚刚从上一个点移动过来的位置 + 1
d[x][y] = d[t.first][t.second] + 1;
// 将当前的位置送进队列
q[++ tt] = {x, y};
//
pre[x][y] = t;
}
}
}
int x = n - 1, y = m - 1;
// 如果当前的位置存在返回的路径
while (x || y){
printf("%d %d\n", x, y);
auto t = pre[x][y];
x = t.first, y = t.second;
}
return d[n - 1][m - 1];
}
int main(){
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
cin >> g[i][j];
cout << bfs() << endl;
return 0;
} -
STL实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 110;
int n, m;
int g[N][N], d[N][N];
int bfs()
{
queue<PII> q;
memset(d, -1, sizeof d);
d[0][0] = 0;
q.push({0, 0});
int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
while (q.size())
{
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ )
{
int x = t.first + dx[i], y = t.second + dy[i];
if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && g[x][y] == 0 && d[x][y] == -1)
{
d[x][y] = d[t.first][t.second] + 1;
q.push({x, y});
}
}
}
return d[n - 1][m - 1];
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
for (int j = 0; j < m; j ++ )
cin >> g[i][j];
cout << bfs() << endl;
return 0;
}
树的深度优先遍历
1 |
|
树的广度优先遍历
树中顶点的层次:
-
STL实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n, m;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
int d[N];
void add(int a, int b)
{
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
int bfs()
{
memset(d, -1, sizeof d);
queue<int> q;
d[1] = 0;
q.push(1);
while (q.size())
{
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (d[j] == -1)
{
d[j] = d[t] + 1;
q.push(j);
}
}
}
return d[n];
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++ )
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
add(a, b);
}
cout << bfs() << endl;
return 0;
} -
模拟队列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int e[N], ne[N], h[N], idx;
int q[N], d[N];
int n, m;
void add(int a, int b){
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}
int bfs(){
q[0] = 1;
memset(d, -1, sizeof d);
d[1] = 0;
int hh = 0, tt = 0;
while(hh <= tt){
int t = q[hh++];
for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
// 表示当前可以到达的点
int j = e[i];
if (d[j] == -1){
d[j] = d[t] + 1;
q[++ tt] = j;
}
}
}
return d[n];
}
int main(){
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int a, b;
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
add(a ,b);
}
printf("%d", bfs());
return 0;
}
拓扑排序
1 |
|
dijkstra求最短路
给定一个n个点m条边的有向图,图中可能存在重边和自环,所有边权均为正值。
请你求出1号点到n号点的最短距离,如果无法从1号点走到n号点,则输出-1。
输入格式
第一行包含整数n和m。
接下来m行每行包含三个整数x,y,z,表示存在一条从点x到点y的有向边,边长为z。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示1号点到n号点的最短距离。
如果路径不存在,则输出-1。
数据范围
1≤n≤5001≤n≤500,
1≤m≤1051≤m≤105,
图中涉及边长均不超过10000。
输入样例:
1 | 3 3 |
输出样例:
1 | 3 |
-
朴素版
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
using namespace std;
const int N = 510, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int g[N][N], dist[N];
bool vis[N];
int m, n;
int dijkstra(){
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int t = -1;
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if (!vis[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j]))
t = j;
if (t == -1) break;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j]);
vis[t] = true;
}
if(dist[n] == INF) return -1;
return dist[n];
}
int main(){
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
memset(g, 0x3f, sizeof g);
while (m--){
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
g[a][b] = min(g[a][b], c);
}
printf("%d\n", dijkstra());
return 0;
} -
堆优化版(如果点和边都在1e5 以上的话需要 堆优化 稀疏图使用邻接表)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
using namespace std;
// first 表示最短的距离, sec表示当前的下标
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m;
int h[N], w[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
int dist[N];
bool vis[N];
void add(int a, int b, int c){
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++;
}
int dijkstra(){
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1] = 0;
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> heap;
heap.push({0, 1});
while(heap.size()){
auto t = heap.top();
heap.pop();
int ver = t.second, dis = t.first;
for (int i = h[ver]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j] > dis + w[i]){
dist[j] = dis + w[i];
heap.push({dist[j], j});
}
}
}
if (dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f) return -1;
return dist[n];
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
while (m--){
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
add(a, b, c);
}
printf("%d", dijkstra());
return 0;
}
Bellman_ford算法
边数限制的最短路:
给定一个n个点m条边的有向图,图中可能存在重边和自环, 边权可能为负数。
请你求出从1号点到n号点的最多经过k条边的最短距离,如果无法从1号点走到n号点,输出impossible。
注意:图中可能 存在负权回路 。
输入格式
第一行包含三个整数n,m,k。
接下来m行,每行包含三个整数x,y,z,表示存在一条从点x到点y的有向边,边长为z。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示从1号点到n号点的最多经过k条边的最短距离。
如果不存在满足条件的路径,则输出“impossible”。
数据范围
1≤n,k≤5001≤n,k≤500,
1≤m≤100001≤m≤10000,
任意边长的绝对值不超过10000。
输入样例:
1 | 3 3 1 |
输出样例:
1 | 3 |
解题代码:
1 |
|
模板
1 | int n, m; // n表示点数,m表示边数 |
SPFA
-
SPFA求最短路问题,同样地, 可以解决dijskstra类的问题,例题代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], w[N], idx;
int dist[N];
bool vis[N];
int n, m;
//链式存储的方式相当于正向的邻接表,以a位起点的一种拉链法相当于 而e[idx] 表示可以走到的点
void add(int a, int b, int c){
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
int spfa(){
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1] = 0;
queue<int> q;
q.push(1);
vis[1] = true;
while(q.size()){
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
// 从队列中出去的时候设置位false
vis[t] = false;
for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
//表示可以到达的点的下标
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i]){
dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i];
if (!vis[j]){
q.push(j);
vis[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
return dist[n];
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
while (m -- ){
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
add(a, b, c);
}
int t = spfa();
if (t == 0x3f3f3f3f) puts("impossible");
else printf("%d\n", t);
return 0;
} -
SPFA判断负环的问题:例题
假设图中n个顶点,添加
cnt数组保存上一个状态过来的边的个数,此依迭代如果出现cnt[i] >= n的话,表示的就是1 - i走存在 至少存在n条边,那么至少走过了n + 1个点,有抽屉原理得到那么至少有一次是走过两次的,一个点走了两次说明存在自环,而在SPFA中求的就是最短路,那么这个环就是负环,所以负环的条件 就是cnt[i] >= n1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
using namespace std;
const int N = 2010, M = 10010;
int n, m;
int h[N], w[M], e[M], ne[M], idx;
int dist[N], cnt[N];
bool vis[N];
void add(int a, int b, int c){
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
int spfa(){
queue<int> q;
// 求整个图中是否存在负环 而不是某一个 起点存在负环
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
vis[i] = true;
q.push(i);
}
while (q.size()){
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
vis[t] = false;
for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i]){
dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i];
cnt[j] = cnt[t] + 1;
if (cnt[j] >= n) return true;
if (!vis[j]){
q.push(j);
vis[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
while (m -- ){
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
add(a, b, c);
}
if (spfa()) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
return 0;
}
Floyd算法
floyd是一种求全局最短的方法 例题
1 |
|
Prim算法
解决最小生成树的问题 注意区分dijkstra,例题:
Prim算法步骤:
- 设置一个集合默认为空,不断添加已经构成的点,假设所有点到此集合的距离为
INF - 找到距离集合最近的点 纳入集合中 设置为 访问过。
- 通过找到的点,更新其他点集合的距离。循环此过程
1 |
|
Kruskal算法
1 |
|
数论
质数
-
试除法求质数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
bool is_prime(int x){
if (x < 2) return false;
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i++){
if (x % i == 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
while (n-- ){
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
if (is_prime(x)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
return 0;
} -
因式分解法求质数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
using namespace std;
void divide(int x)
{
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )
if (x % i == 0)
{
int s = 0;
while (x % i == 0) x /= i, s ++ ;
cout << i << ' ' << s << endl;
}
if (x > 1) cout << x << ' ' << 1 << endl;
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n -- )
{
int x;
cin >> x;
divide(x);
}
return 0;
} -
筛法求质数(朴素)
筛质数: 给定一个正整数n,请你求出1~n中质数的个数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
const int N = 10000010;
bool st[N];
int prime[N], cnt;
void get_primes(int n){
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
if(!st[i]) prime[cnt++] = n;
for (int j = i + i; j <= n; j += i) st[j] = true;
}
}
int main(){
int n;
scanf ("%d", &n);
get_primes(n);
printf("%d", cnt);
return 0;
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
using namespace std;
const int N= 1000010;
int primes[N], cnt;
bool st[N];
void get_primes(int n)
{
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++ )
{
if (st[i]) continue;
primes[cnt ++ ] = i;
for (int j = i; j <= n; j += i)
st[j] = true;
}
}
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
get_primes(n);
cout << cnt << endl;
return 0;
} -
线性筛法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
using namespace std;
const int N= 1000010;
int primes[N], cnt;
bool st[N];
void get_primes(int n)
{
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++ )
{
if (!st[i]) primes[cnt ++ ] = i;
for (int j = 0; primes[j] <= n / i; j ++ )
{
st[primes[j] * i] = true;
if (i % primes[j] == 0) break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
get_primes(n);
cout << cnt << endl;
return 0;
}
约数
-
最大公约数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
int gcd(int a, int b){
return a % b == 0 ? b : gcd(b, a % b);
}
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
while(n --){
int a, b;
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
printf("%d\n", gcd(a, b));
}
return 0;
}
动态规划
背包问题
背包问题是动态规划问题中的典型问题,具体如下几种解析: 一般的思路方法
MATHJAX-SSR-3
-
01背包问题
-
动态规划的二维写法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
// m 表示物品的数量, N表示背包的容量
int m, n;
int dp[N][N], w[N], v[N];
int main(){
cin >> m >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cin >> v[i] >> w[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
if (j >= v[i])
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j - v[i]] + w[i]);
}
}
cout << dp[m][n];
return 0;
} -
优化为一维的写法
对于滚动数组的理解:由二维的数组可知,我们每一层中的dp[i] 是由dp[i - 1]计算得到的,dp[i]又是从左半边的 到的,那么我们就可以从末尾计算过程,右边不满足条件的不计算过程将 dp[i - 1]左边和 dp[i]的右边拼接起来,这样的方式就是滚动数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
// m 表示物品的数量, N表示背包的容量
int m, n;
int dp[N], w[N], v[N];
int main(){
cin >> m >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cin >> v[i] >> w[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
for (int j = n; j >= v[i]; j--)
dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - v[i]] + w[i]);
cout << dp[n];
return 0;
}
-
-
完全背包问题
同一种物品可以选择多次,那么我们就枚举可以K次选择,类似于01背包问题
-
朴素版本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
// m 表示物品的数量, N表示背包的容量
int m, n;
int dp[N][N], w[N], v[N];
int main(){
cin >> m >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cin >> v[i] >> w[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++)
for (int k = 0; k * v[i] <= j; k++)
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j - v[i] * k] + k * w[i]);
cout << dp[m]n];
return 0;
}优化版本 :(不同于滚动数组 这里是正向 枚举)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
// m 表示物品的数量, N表示背包的容量
int m, n;
int dp[N], w[N], v[N];
int main(){
cin >> m >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cin >> v[i] >> w[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
for (int j = v[i]; j <= n; j++)
dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - v[i]] + w[i]);
cout << dp[n];
return 0;
}
-
-
多重背包问题
-
多重背包的朴素版本
通过完全背包的思路的启发对于每种的物品最多只能选择s[i]次,我们将刚刚的k改为s[i]即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
// m 表示物品的数量, N表示背包的容量
int m, n;
int dp[N][N], w[N], v[N], s[N];
int main(){
cin >> m >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cin >> v[i] >> w[i] >> s[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++)
for (int k = 0; k * v[i] <= j && k <= s[i]; k++)
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j - v[i] * k] + k * w[i]);
cout << dp[m][n];
return 0;
} -
多重背包的优化 : 二进制优化方案
对于每种物品存在有多种选择时:思考一个问题 是否需要一一枚举每种可能? 如果选择的物品的种类 为1k次, 容量为1k, 每种选择为次数最大为1k 此时 时间复杂为 此时最高的计算次数就是1E,在C++中此时一般给定的用时为1s,此时就会出现TLE, 对此需要对其进行优化
优化方法:在此之前我们考虑 IPv4地址 表示方式使用的是32为二进制表示,每八位使用一个点一分割, 这样的方法称为点分十进制方法表示,那么其中每八位通过十进制表示的数据范围是0-255即(),对于这里我们并没有一一枚举,而是通过每位不同位上的二进制表示,通过八个01分别代表十进制数 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1其中 选或者不选的方法组合表示 0 - 255其中任何一个数字,那么回归到我们的多重背包问题将给定的是s[i]可以选择的数量用同样的方法分解,假设 对于s[i]的最大值位255,那么我们就可以分八组128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 计算, 但是对于s[i]的值不可能凑巧是, 那么多余的部分就 用 , 假设s[i]位 280,那么添加多的一个分组的数字就是 25 此时组成的数据就是128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 25 此时就可有组成 0- 280之间的任何一个数字, 分组之后最每个组做一次 01背包问题即可 。
证明此过程
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
using namespace std;
const int N = 12010, M = 2010;
int n, m;
int v[N], w[N];
int f[M];
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
int a, b, s;
cin >> a >> b >> s;
int k = 1;
while (k <= s)
{
cnt ++ ;
v[cnt] = a * k;
w[cnt] = b * k;
s -= k;
k *= 2;
}
if (s > 0)
{
cnt ++ ;
v[cnt] = a * s;
w[cnt] = b * s;
}
}
n = cnt;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = m; j >= v[i]; j -- )
f[j] = max(f[j], f[j - v[i]] + w[i]);
cout << f[m] << endl;
return 0;
}
-
-
分组背包问题
将多个物品分租,每组中只能选择一个物品: 存在不理解的地方 需要回顾
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int n, m;
int v[N][N], w[N][N], s[N];
int dp[N];
int main(){
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
cin >> s[i];
for (int j = 0; j < s[i]; j ++ )
cin >> v[i][j] >> w[i][j];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = m; j >= 0; j -- )
for (int k = 0; k < s[i]; k ++ )
if (v[i][k] <= j)
dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - v[i][k]] + w[i][k]);
cout << dp[m] << endl;
return 0;
}
线性dp
-
数字三角形问题
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
using namespace std;
const int N = 510, INF = 1e9;
int n;
int a[N][N];
int f[N][N];
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j ++ )
scanf("%d", &a[i][j]);
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 0; j <= i + 1; j ++ )
f[i][j] = -INF;
f[1][1] = a[1][1];
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j ++ )
f[i][j] = max(f[i - 1][j - 1] + a[i][j], f[i - 1][j] + a[i][j]);
int res = -INF;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) res = max(res, f[n][i]);
printf("%d\n", res);
return 0;
} -
最长上升子序列问题(LeetCode 300)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int n;
int a[N], f[N];
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
f[i] = 1; // 只有a[i]一个数
for (int j = 1; j < i; j ++ )
if (a[j] < a[i])
f[i] = max(f[i], f[j] + 1);
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) res = max(res, f[i]);
printf("%d\n", res);
return 0;
} -
最长公共子序列问题(1.11mins)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int n, m;
char a[N], b[N];
int f[N][N];
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
scanf("%s%s", a + 1, b + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ )
{
f[i][j] = max(f[i - 1][j], f[i][j - 1]);
if (a[i] == b[j]) f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j - 1] + 1);
}
printf("%d\n", f[n][m]);
return 0;
}
区间dp
动态规划
石子合并问题
1 |
|
计数类dp
数位统计dp
状态压缩dp
-
分割问题:
求把NM的棋盘分割成若干个12的的长方形,有多少种方案。
例如当N=2,M=4时,共有5种方案。当N=2,M=3时,共有3种方案。
如下图所示:

输入格式
输入包含多组测试用例。
每组测试用例占一行,包含两个整数N和M。
当输入用例N=0,M=0时,表示输入终止,且该用例无需处理。
输出格式
每个测试用例输出一个结果,每个结果占一行。
数据范围
1≤N,M≤111≤N,M≤11
输入样例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
91 2
1 3
1 4
2 2
2 3
2 4
2 11
4 11
0 0输出样例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
81
0
1
2
3
5
144
51205解题代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
using namespace std;
const int N = 12, M = 1 << N;
int n, m;
long long f[N][M];
bool st[M];
int main()
{
while (cin >> n >> m, n || m)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 1 << n; i ++ )
{
int cnt = 0;
st[i] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j ++ )
if (i >> j & 1)
{
if (cnt & 1) st[i] = false;
cnt = 0;
}
else cnt ++ ;
if (cnt & 1) st[i] = false;
}
memset(f, 0, sizeof f);
f[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ )
for (int j = 0; j < 1 << n; j ++ )
for (int k = 0; k < 1 << n; k ++ )
if ((j & k) == 0 && st[j | k])
f[i][j] += f[i - 1][k];
cout << f[m][0] << endl;
}
return 0;
} -
最短Hamilton路径
给定一张 nn 个点的带权无向图,点从 0~n-1 标号,求起点 0 到终点 n-1 的最短Hamilton路径。 Hamilton路径的定义是从 0 到 n-1 不重不漏地经过每个点恰好一次。
输入格式
第一行输入整数nn。
接下来nn行每行nn个整数,其中第ii行第jj个整数表示点ii到jj的距离(记为a[i,j])。
对于任意的x,y,zx,y,z,数据保证 a[x,x]=0,a[x,y]=a[y,x] 并且 a[x,y]+a[y,z]>=a[x,z]。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示最短Hamilton路径的长度。
数据范围
1≤n≤201≤n≤20
0≤a[i,j]≤1070≤a[i,j]≤107输入样例:
1
2
3
4
5
65
0 2 4 5 1
2 0 6 5 3
4 6 0 8 3
5 5 8 0 5
1 3 3 5 0输出样例:
1
18
解题代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
using namespace std;
const int N = 20, M = 1 << N;
int n;
int w[N][N];
int f[M][N];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
for (int j = 0; j < n; j ++ )
cin >> w[i][j];
memset(f, 0x3f, sizeof f);
f[1][0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 1 << n; i ++ )
for (int j = 0; j < n; j ++ )
if (i >> j & 1)
for (int k = 0; k < n; k ++ )
if (i >> k & 1)
f[i][j] = min(f[i][j], f[i - (1 << j)][k] + w[k][j]);
cout << f[(1 << n) - 1][n - 1];
return 0;
}
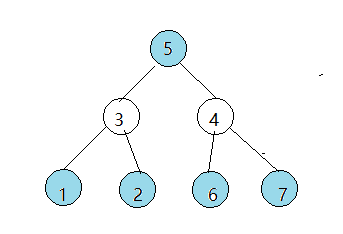
树形dp
Ural大学有N名职员,编号为1~N。
他们的关系就像一棵以校长为根的树,父节点就是子节点的直接上司。
每个职员有一个快乐指数,用整数 HiHi 给出,其中 1≤i≤N1≤i≤N。
现在要召开一场周年庆宴会,不过,没有职员愿意和直接上司一起参会。
在满足这个条件的前提下,主办方希望邀请一部分职员参会,使得所有参会职员的快乐指数总和最大,求这个最大值。
输入格式
第一行一个整数N。
接下来N行,第 i 行表示 i 号职员的快乐指数HiHi。
接下来N-1行,每行输入一对整数L, K,表示K是L的直接上司。
输出格式
输出最大的快乐指数。
数据范围
1≤N≤60001≤N≤6000,
−128≤Hi≤127−128≤Hi≤127
输入样例:
1 | 7 |
输出样例:
1 | 5 |
解题代码 以思路
每个人都存在上司,其中每个职员都不想 和自己的直接上司组合的一起,在这情况下,找到参会职员的快乐值的最大值, 其实就是树形的结构中找到没有直接根节点的能组合个个数 以题中的案例为解释
其中蓝色的就是可以组合的值:
实现的思路:
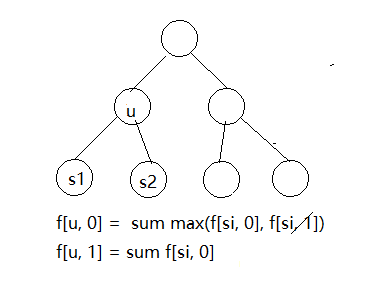
以上图为例:f[u, 0]这个状态表示的当前的根结点没有选择的方案,而f[u, 1]表示当前的根节点已经选择的方案,再此之前需要计算每一个子节点的状态分别为 f[s1, 0], f[s1, 1], f[s2, 0], f2[s2, 1] (每个步骤是需要使用递归求解的)
计算步骤:
- f[u, 0] 包含了以u为根节点全部的子树,此时需要是子树的每个节点都是最大的值,当u不选的时候,那么它的自己点是可以选择或者不选的f[u, 0] = sum max(f[si, 0], f[si, 1]) , (si表示所有的子节点, 即边的数量 )
- f[u, 1] 表示 当前的根节点选择,此时表示它的子节点不能选择 f[u, 1] = sum f[si, 0]
解题代码:
1 |
|
记忆化搜索
给定一个R行C列的矩阵,表示一个矩形网格滑雪场。
矩阵中第 i 行第 j 列的点表示滑雪场的第 i 行第 j 列区域的高度。
一个人从滑雪场中的某个区域内出发,每次可以向上下左右任意一个方向滑动一个单位距离。
当然,一个人能够滑动到某相邻区域的前提是该区域的高度低于自己目前所在区域的高度。
下面给出一个矩阵作为例子:
1 | 1 2 3 4 5 |
在给定矩阵中,一条可行的滑行轨迹为24-17-2-1。
在给定矩阵中,最长的滑行轨迹为25-24-23-…-3-2-1,沿途共经过25个区域。
现在给定你一个二维矩阵表示滑雪场各区域的高度,请你找出在该滑雪场中能够完成的最长滑雪轨迹,并输出其长度(可经过最大区域数)。
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数R和C。
接下来R行,每行包含C个整数,表示完整的二维矩阵。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示可完成的最长滑雪长度。
数据范围
1≤R,C≤3001≤R,C≤300,
0≤矩阵中整数≤100000≤矩阵中整数≤10000
输入样例:
1 | 5 5 |
输出样例:
1 | 25 |
题目大意 解题思路
在给定的矩阵中,由高的点向下移动,求可以移动的最大的距离,通过之前使用的就是dfs的思路解题,一般dfs是都是可以 转化为dp求解的,但是这种通过dfs求解的方式使用循环的方式数组保存状态相对复杂, 在这里就是用记忆化搜索来解题,一般的dfs我们是没有将原来的状态保存的,所以每一次计算搜需要向前依次计算此过程,存在多余的计算,但是现在我们使用记忆化搜索就是通过一个额外的矩阵保存当前的状态,每次需要计算的时候直接返回当前的值,这样的过程称为 记忆化搜索。 简单来说就是dfs计算值并保存 保存状态 下次计算如果存在直接返回已经计算的值。
对应到本题,存在四个方向,每个方向都是可能走的但是需要满足比上一个位置的值小的条件。如果满足的话,就在上一个位置的基础上+1,最终找到最优解
解题代码
1 |
|
贪心
关于一些贪心的问题题目
区间贪心
-
区间选点问题
给定N个闭区间[ai,biai,bi],请你在数轴上选择尽量少的点,使得每个区间内至少包含一个选出的点。
输出选择的点的最小数量。
位于区间端点上的点也算作区间内。
输入格式
第一行包含整数N,表示区间数。
接下来N行,每行包含两个整数ai,biai,bi,表示一个区间的两个端点。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示所需的点的最小数量。
数据范围
1≤N≤1051≤N≤105,
−109≤ai≤bi≤109−109≤ai≤bi≤109输入样例:
1
2
3
43
-1 1
2 4
3 5输出样例:
1
2
解题步骤
- 将每个区间按照右端点 由小到大排序
- 从前向后 枚举每个区间 如果区间出现过 pass 否则选择当前区间的右端点
证明
- 假设ans为答案 为方案中最小的值 cnt为计数变量 为可行的方案所以存在 ans <= cnt
- 当出现第二种情况的时候 ,当找到cnt个点时候,从左到右一次排好,并且没有交集,一个点 每次最多只能覆盖一个区间, 所以至少需要 cnt 个点(或更多) 即 ans >= cnt
- 由以上两条 ans == cnt 就是需要输出的答案
解题代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n;
struct Range
{
int l, r;
bool operator< (const Range &W)const
{
return r < W.r;
}
}range[N];
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) scanf("%d%d", &range[i].l, &range[i].r);
sort(range, range + n);
int res = 0, ed = -2e9;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
if (range[i].l > ed)
{
res ++ ;
ed = range[i].r;
}
printf("%d\n", res);
return 0;
} -
区间不覆盖问题证明 33mins
解题分析同上
-
区间分组(证明 54mins)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n;
struct Range
{
int l, r;
bool operator< (const Range &W)const
{
return l < W.l;
}
}range[N];
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
int l, r;
scanf("%d%d", &l, &r);
range[i] = {l, r};
}
sort(range, range + n);
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> heap;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
auto r = range[i];
if (heap.empty() || heap.top() >= r.l) heap.push(r.r);
else
{
heap.pop();
heap.push(r.r);
}
}
printf("%d\n", heap.size());
return 0;
} -
区间覆盖问题
给定N个闭区间[ai,biai,bi]以及一个线段区间[s,ts,t],请你选择尽量少的区间,将指定线段区间完全覆盖。
输出最少区间数,如果无法完全覆盖则输出-1。
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数s和t,表示给定线段区间的两个端点。
第二行包含整数N,表示给定区间数。
接下来N行,每行包含两个整数ai,biai,bi,表示一个区间的两个端点。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示所需最少区间数。
如果无解,则输出-1。
数据范围
1≤N≤1051≤N≤105,
−109≤ai≤bi≤109−109≤ai≤bi≤109,
−109≤s≤t≤109−109≤s≤t≤109输入样例:
1
2
3
4
51 5
3
-1 3
2 4
3 5输出样例:
1
2
解题思路:
步骤:
-
将所有的区间按照左端点有小到大排序
-
从前往后依次枚举每个区间,能在所有能覆盖start区间中,选择右端点最大的区间之后将start更新为右端点的最大值
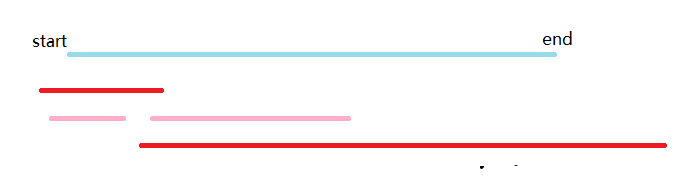

其中蓝色为目标区间,红色为需要选定的区间
证明:
假设 ans为最小的区间个数的结果,而cnt为所有解其中之一的结果,此时就是cnt >= ans的也就是说cnt 中包含的区间个数是多于ans中区间的个数的,通过我们的算法是可以不断找最优解的过程最终使得 ans == cnt 最终答案就是所求
解题代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n;
struct Range
{
int l, r;
bool operator< (const Range &W)const
{
return l < W.l;
}
}range[N];
int main()
{
int st, ed;
scanf("%d%d", &st, &ed);
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
int l, r;
scanf("%d%d", &l, &r);
range[i] = {l, r};
}
sort(range, range + n);
int res = 0;
bool success = false;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
int j = i, r = -2e9;
while (j < n && range[j].l <= st)
{
r = max(r, range[j].r);
j ++ ;
}
if (r < st)
{
res = -1;
break;
}
res ++ ;
if (r >= ed)
{
success = true;
break;
}
st = r;
i = j - 1;
}
if (!success) res = -1;
printf("%d\n", res);
return 0;
} -
Huffman树贪心
-
果子合并问题(经典的Huffman问题)
在一个果园里,达达已经将所有的果子打了下来,而且按果子的不同种类分成了不同的堆。
达达决定把所有的果子合成一堆。
每一次合并,达达可以把两堆果子合并到一起,消耗的体力等于两堆果子的重量之和。
可以看出,所有的果子经过n-1次合并之后,就只剩下一堆了。
达达在合并果子时总共消耗的体力等于每次合并所耗体力之和。
因为还要花大力气把这些果子搬回家,所以达达在合并果子时要尽可能地节省体力。
假定每个果子重量都为1,并且已知果子的种类数和每种果子的数目,你的任务是设计出合并的次序方案,使达达耗费的体力最少,并输出这个最小的体力耗费值。
例如有3种果子,数目依次为1,2,9。
可以先将1、2堆合并,新堆数目为3,耗费体力为3。
接着,将新堆与原先的第三堆合并,又得到新的堆,数目为12,耗费体力为12。
所以达达总共耗费体力=3+12=15。
可以证明15为最小的体力耗费值。
输入格式
输入包括两行,第一行是一个整数n,表示果子的种类数。
第二行包含n个整数,用空格分隔,第i个整数aiai是第i种果子的数目。
输出格式
输出包括一行,这一行只包含一个整数,也就是最小的体力耗费值。
输入数据保证这个值小于231231。
数据范围
1≤n≤100001≤n≤10000,
1≤ai≤200001≤ai≤20000输入样例:
1
23
1 2 9输出样例:
1
15
题目大意:
在给定的集合中,存在不同权值的点, 将他们构建成Huffman树,输出每次需要合并的权值,同过优先队列实现组合权值的过程即可。
证明:
主要证明两点如下:
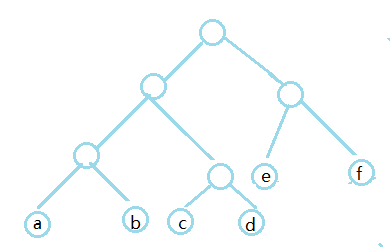
-
权值最小的两个点,深度一定是最深的,且可以互为兄弟
总的权值为 3(a + b + c + d) + 2(e + f)
此时假设 a , f 为最小的权值 b 并不为最小的 ,那么这两个局部的 交换之前是 2f + 3b
之后是 3 f + 2b 前后相减得到b - f > 0 所以 交换是有意义的。
-
当两个点合并之后,对于之前的n个点,那么就是 n - 1个点的Huffman问题,f(n) = f(n - 1) + a + b , 此时计算f(n - 1)即可 根据证明1,不断循环重复此过程,实现最后求解
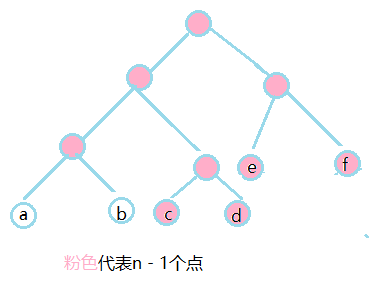
解题代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> heap;
while (n -- )
{
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
heap.push(x);
}
int res = 0;
while (heap.size() > 1)
{
int a = heap.top(); heap.pop();
int b = heap.top(); heap.pop();
res += a + b;
heap.push(a + b);
}
printf("%d\n", res);
return 0;
} -
排序不等式
例题:
有 nn 个人排队到 1 个水龙头处打水,第 ii 个人装满水桶所需的时间是 titi,请问如何安排他们的打水顺序才能使所有人的等待时间之和最小?
输入格式
第一行包含整数 nn。
第二行包含 nn 个整数,其中第 ii 个整数表示第 ii 个人装满水桶所花费的时间 titi。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示最小的等待时间之和。
数据范围
1≤n≤1051≤n≤105,
1≤ti≤1041≤ti≤104
输入样例:
1 | 7 |
输出样例:
1 | 56 |
解题思路
给定不同同学排队的时间,使他们依次排在后排队方法,求总共排序 的时间
3 6 1 4 2 5 7
3 * 6 + 6 * 5 + 1 * 4 + 4 * 3 + 2 * 2 + 5 * 1
规律
证明:从某一项开始,不是单调递增未排序的 那么存在 可以交换
交换之前:
交换之后:
所以就是交换完之后序列的最优解方案就是时间单调递增的序列。
解题代码
1 |
|
绝对值不等式
在一条数轴上有 NN 家商店,它们的坐标分别为 A1A1~ANAN。
现在需要在数轴上建立一家货仓,每天清晨,从货仓到每家商店都要运送一车商品。
为了提高效率,求把货仓建在何处,可以使得货仓到每家商店的距离之和最小。
输入格式
第一行输入整数N。
第二行N个整数A1A1~ANAN。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示距离之和的最小值。
数据范围
1≤N≤1000001≤N≤100000
输入样例:
1 | 4 |
输出样例:
1 | 12 |
题目解析
题目中要求找到距离之的最小值
-
每个点到货舱的位置就是方程表示为
-
对应的项分组表示为:
-
对应现在一个点(选定的地址)两边存在两个点,使他们之间的距离之和最小, **距离最小的时候为 选定的地址在 两个仓库(左侧为b, 右侧为a)之间,他们的距离为 b-a **
-
对于每项都有
-
如果 第一项成立的话 x的位置在 xn 和 x1之间, 第二项同理,如果使没项都成立的话,意味着每项都在对应的中间位置,所以仓库的位置就是最中间位置(中位数),如果使偶数的,中间两个之间。
推理的过程:
解题代码
1 |
|
推公式
题目(59mins)
农民约翰的N头奶牛(编号为1…N)计划逃跑并加入马戏团,为此它们决定练习表演杂技。
奶牛们不是非常有创意,只提出了一个杂技表演:
叠罗汉,表演时,奶牛们站在彼此的身上,形成一个高高的垂直堆叠。
奶牛们正在试图找到自己在这个堆叠中应该所处的位置顺序。
这N头奶牛中的每一头都有着自己的重量WiWi以及自己的强壮程度SiSi。
一头牛支撑不住的可能性取决于它头上所有牛的总重量(不包括它自己)减去它的身体强壮程度的值,现在称该数值为风险值,风险值越大,这只牛撑不住的可能性越高。
您的任务是确定奶牛的排序,使得所有奶牛的风险值中的最大值尽可能的小。
输入格式
第一行输入整数N,表示奶牛数量。
接下来N行,每行输入两个整数,表示牛的重量和强壮程度,第i行表示第i头牛的重量WiWi以及它的强壮程度SiSi。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示最大风险值的最小可能值。
数据范围
1≤N≤500001≤N≤50000,
1≤Wi≤10,0001≤Wi≤10,000,
1≤Si≤1,000,000,0001≤Si≤1,000,000,000
输入样例:
1 | 3 |
输出样例:
1 | 2 |
题目解析:
类似于排序不等式的证明问题,
按照 wi + si 从小到大顺序排,最带的危险的系数一定使最小的
解题代码
1 |
|
时间复杂度分析
一般ACM或者笔试题的时间限制是1秒或2秒。
在这种情况下,C++代码中的操作次数控制在 107107 为最佳。
下面给出在不同数据范围下,代码的时间复杂度和算法该如何选择:
一般ACM或者笔试题的时间限制是1秒或2秒。
在这种情况下,C++代码中的操作次数控制在 107107 为最佳。
下面给出在不同数据范围下,代码的时间复杂度和算法该如何选择:
n≤30n≤30, 指数级别, dfs+剪枝,状态压缩dp
n≤100n≤100 => O(n3)O(n3),floyd,dp
n≤1000n≤1000 => O(n2)O(n2),O(n2logn)O(n2logn),dp,二分
n≤10000n≤10000 => O(n∗n√)O(n∗n),块状链表
n≤100000n≤100000 => O(nlogn)O(nlogn) => 各种sort,线段树、树状数组、set/map、heap、dijkstra+heap、spfa、求凸包、求半平面交、二分
n≤1000000n≤1000000 => O(n)O(n), 以及常数较小的 O(nlogn)O(nlogn) 算法 => hash、双指针扫描、kmp、AC自动机,常数比较小的 O(nlogn)O(nlogn) 的做法:sort、树状数组、heap、dijkstra、spfa
n≤10000000n≤10000000 => O(n)O(n),双指针扫描、kmp、AC自动机、线性筛素数
n≤109n≤109 => O(n√)O(n),判断质数
n≤1018n≤1018 => O(logn)O(logn),最大公约数

代码时间复杂度
-
循环层数 层数 对应平方数
例如背包问题就是 on2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
// m 表示物品的数量, N表示背包的容量
int m, n;
int dp[N][N], w[N], v[N];
int main(){
cin >> m >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cin >> v[i] >> w[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
if (j >= v[i])
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j - v[i]] + w[i]);
}
}
cout << dp[m][n];
return 0;
} -
递归 例如快速排序 每层 n 个 存在 log n 层 NlogN
1 | void quicksort(int q[], int l, int r){ |
二分 对应 一层 log n
-
kmp 22mins, on
-
并查集 nlogn
-
搜索dfs问题 全排列问题(28mins)
计算函数执行的次数 树的最后一层就是 总共 n!个点 每一层计算 输出需要on的复杂度

-
图的深度 或者 宽度 的 n 点 m边 o(m + n)
-
对优化dijkstra
m(边的数量)* logm (对应边的m 操作此时) 对应的边 n^2 近似看成 mlogm
1
2
3
4
5
6
7for (int i = h[ver]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j] > dis + w[i]){
dist[j] = dis + w[i];
heap.push({dist[j], j});
}
} -
belman o(n^2) spfa o (n*m) 32mins
-
kruskal mlogm 并查集 om
-
染色法 二分图 匈牙利 34mins
-
因为l
-
数学中的问题 35mins
-
状态压缩 dp 40mins 蒙德里安的梦想 2 ^2n * n
-
树型 dp 就是 树种每个结点的数量,因为只遍历依次
-
动态规划问题 复杂度 就是 状态数量 * 每个状态的计算量
滑雪问题 状态数量 on^2
- 分组背包问题 状态的数量 o nm * 状态的计算量 o k

